Ensuring the long-term reliability of modern infrastructure requires more than routine inspections and periodic maintenance. As structures become more complex and are expected to perform under harsher environmental and operational conditions, engineers are increasingly turning to advanced sensing technologies to capture what cannot be seen with the naked eye. Among these technologies, Distributed Temperature Stress Detectors (DTSD)—powered by distributed optical fiber systems—have become one of the most effective tools for monitoring temperature, strain, and stress variations along critical assets.
Shenzhen Mingsheng Electrical Co., Ltd., a company that has spent years developing fiber-optic sensing equipment and full-stack monitoring solutions, provides a suite of advanced products that make DTSD deployment both practical and scalable. Their portfolio includes distributed fiber-optic sensing devices (DTS, DAS, DVS, BOTDA, BOTDR), fiber-optic transformers, fiber Bragg grating systems, fluorescence fiber sensing equipment, and a wide range of temperature-sensing cables. These tools offer the foundation for precise, real-time structural integrity monitoring across industries such as power, energy storage, transportation, and industrial safety.
This article explores how distributed temperature stress detectors work, why they are transforming structural health monitoring, and how companies like Shenzhen Mingsheng Electrical Co., Ltd. integrate them into comprehensive safety and monitoring solutions.
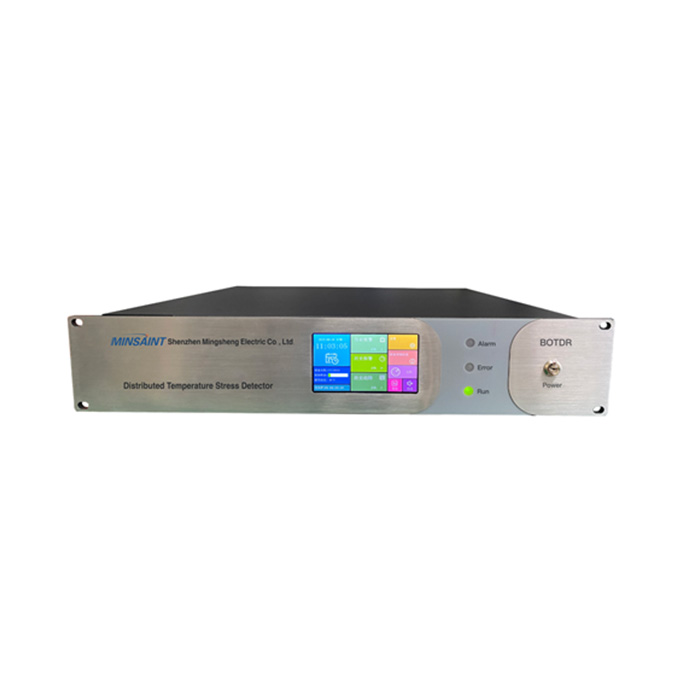

What Makes Distributed Temperature Stress Detection Unique?
Unlike traditional sensors that measure conditions only at specific points, distributed systems leverage optical fibers to capture temperature or strain data continuously along the entire length of the cable. This enables engineers to detect early warning signs of stress accumulation, thermal anomalies, and potential structural failures before they escalate into critical problems.
Technologies such as BOTDA (Brillouin Optical Time Domain Analysis) and BOTDR (Brillouin Optical Time Domain Reflectometry) allow sensing on long-distance fibers with high resolution. For applications requiring single-ended access—such as buried pipelines or long tunnels—users can integrate solutions like the BOTDR-based system linked below:<a href="https://www.minsaint.com/distributed-temperature-stress-botdr-single-ended-measurement.html">Distributed Temperature & Stress BOTDR Single-Ended Measurement</a>
This type of setup reduces installation constraints and simplifies monitoring in locations where fibers cannot be looped or accessed from both ends.
Key Functions of Temperature Stress Detectors
1. Continuous Thermal Monitoring
Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS) technology measures temperature changes along fiber cables with meter-level accuracy. This function is critical in systems where local overheating can propagate rapidly, such as high-voltage cable tunnels, lithium battery packs, or large industrial facilities.
2. Strain and Stress Profiling
With BOTDA/BOTDR, strain profiles can be mapped in real time. This helps engineers identify stress concentrations caused by loading changes, ground movement, material fatigue, or external impact.
3. Early Fault Detection
By observing the interaction between temperature and mechanical stress, DTSD systems can identify early-stage anomalies such as insulation degradation, micro-cracks, corrosion-induced deformation, thermal runaway in batteries, or leakage spots in pipelines.
4. Long-Distance Coverage
Optical fibers can extend over tens of kilometers, enabling a single system to replace thousands of discrete sensors while providing richer data and easier maintenance.
Practical Applications that Enhance Structural Integrity
Shenzhen Mingsheng Electrical Co., Ltd. integrates its fiber-optic technologies into multiple real-world monitoring solutions. These solutions demonstrate how distributed sensing improves safety, reduces downtime, and optimizes asset management.
1. Lithium Battery Rack Fire Detection
Lithium battery systems are increasingly used for energy storage, yet they bring risks such as thermal runaway and localized overheating. Distributed temperature measurement enables early detection of abnormal heat patterns inside battery racks. By identifying temperature rise at its earliest stage, operators can isolate affected modules and prevent escalation.
2. Power Grid and Electrical Fire Early Monitoring
Electric cables, switchgear rooms, and substations require precise thermal monitoring to identify loose connections, overloads, or insulation failures. Optical fibers installed near cables can detect hotspots instantly.
Mingsheng’s electrical fire early detection systems leverage optical fibers to offer rapid response, especially in high-risk environments like dense cable trays and enclosed tunnels.
3. Pipeline Safety Warning Systems
Pipelines carrying oil, gas, chemicals, or water face threats such as corrosion, ground movement, overpressure, and external intrusion. Fiber-optic stress sensing helps:
Detect leakage through temperature anomalies
Monitor strain caused by soil settlement
Identify external interference
Prevent structural breakouts
By continuously observing the stress distribution, operators can make data-driven maintenance decisions and avoid catastrophic failure.
4. LNG / Large Storage Tank Temperature Monitoring
Storage tanks—especially LNG tanks—experience temperature gradients that need precise monitoring to avoid internal stress imbalance. Distributed sensing reveals temperature layers inside the tank, ensuring safe operation and preventing structural fatigue.
5. Highway and Subsea Tunnel Monitoring
Tunnels require continuous monitoring for fire hazards, heat buildup, deformation, and micro-crack development. Fiber-optic systems embedded in the lining allow operators to detect stress concentration long before visible signs appear.
6. Grain Warehouse Temperature Sensing
Temperature plays a critical role in grain quality. Unexpected heat rise can signal fermentation, moisture imbalance, or early fire risk. Distributed sensors track conditions across large storage areas, enabling operators to act early and maintain food safety.
7. Building and Industrial Facility Fire Detection
Modern buildings rely on optical fiber fire detection to observe cable tunnels, equipment rooms, underground spaces, and high-risk industrial areas. Distributed sensing delivers rapid and accurate alerts, even in environments where conventional detectors struggle due to dust, humidity, or airflow challenges.
8. Synesthesia Technology Systems
Shenzhen Mingsheng integrates distributed sensing with AI-driven interpretation, multi-sensor fusion, and real-time risk modeling. Synesthesia systems correlate data from temperature, vibration, acoustics, and strain sensors to create a more complete picture of structural health.
How Distributed Sensing Improves Structural Integrity Throughout the Asset Lifecycle
During Design
Engineers can simulate load conditions and use distributed sensing data to validate structural assumptions. This leads to better material selection and design optimization.
During Construction
DTSD systems provide real-time monitoring of stress and temperature during critical construction acts such as concrete curing, tunnel excavation, and pipeline laying.
During Operation
The system acts as an always-on diagnostic tool. It ensures that any change—thermal, mechanical, or environmental—is captured and interpreted instantly.
During Maintenance
Maintenance teams receive precise location-based information, enabling targeted repairs instead of broad or reactive maintenance routines.
Why Companies Choose Shenzhen Mingsheng Electrical Co., Ltd.
Mingsheng’s sensor product ecosystem covers:
Distributed fiber optic sensing devices: DTS, DAS, DVS, BOTDA, BOTDR
Fiber-optic mutual inductance equipment
Fiber Bragg grating sensing devices
Fluorescence fiber sensing systems
Specialized temperature-sensing cables
Their engineering teams customize complete solutions for diverse sectors, offering reliability, stability, and long-distance measurement capability. By integrating advanced algorithms with high-quality optical equipment, the company delivers monitoring systems that are dependable, scalable, and practical for real-world environments.
Future Trends: Toward Smarter Structural Monitoring
As infrastructure ages and environmental challenges intensify, distributed sensing will become a standard component of asset management. Key future developments include:
Integration with cloud-based analytics
AI-powered predictive maintenance
More robust fiber materials for extreme environments
Hybrid sensing combining temperature, strain, vibration, and acoustic analysis
Wider adoption in smart cities and intelligent industrial clusters
Distributed temperature stress detectors will continue to shape how organizations maintain safe, efficient, and resilient structures.
Conclusion
Distributed Temperature Stress Detectors represent a significant advancement in structural monitoring. With continuous, precise, and long-distance data capture, they allow engineers and operators to detect problems before they become failures. Shenzhen Mingsheng Electrical Co., Ltd. further enhances the value of this technology through its extensive line of distributed fiber-optic sensors and integrated monitoring solutions across power, energy storage, transportation, industrial facilities, and environmental safety.
As industries aim for higher safety standards and longer asset lifecycles, distributed fiber-optic sensing will play an increasingly central role in ensuring structural integrity.
www.minsaint.com
Shenzhen Mingsheng Electrical Co ., Ltd. ( MINSAINT)