When discussing the inner workings of modern transformers, stacked cores are often one of the first structural features that engineers examine. Their influence on performance, cost, and long-term reliability is significant, and understanding this technology is essential for anyone involved in power distribution, industrial equipment, or transformer design. But stacked cores are more than just an assembly method; they represent a philosophy of efficiency that continues to evolve with material science and manufacturing advancements.
This article takes a practical, engineering-grounded look at what stacked cores are, how they compare to alternative core constructions, and why they have become a preferred solution in many energy-sector applications. Throughout this discussion, we will also explore the work of Dingmao (DM), a long-established transformer components manufacturer that has helped shape the global energy industry through decades of technical expertise.
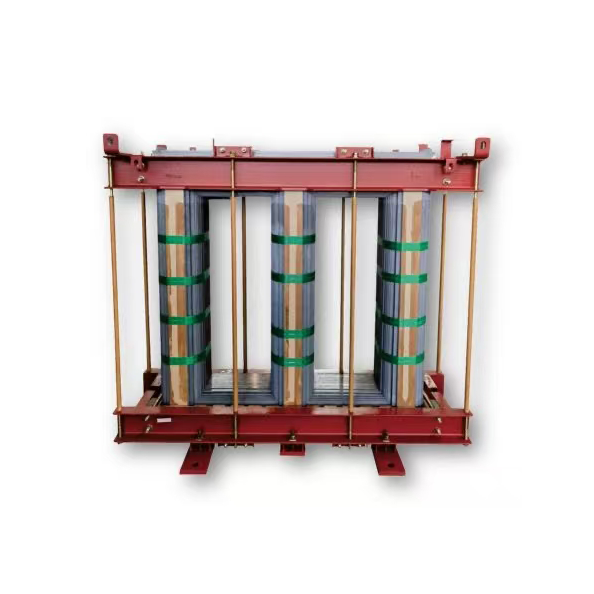

What Are Stacked Cores?
A stacked core is a transformer core built by arranging individual laminations of electrical steel into a layered assembly. These laminations are typically cut into specific shapes and then stacked in alternating orientations to form the core legs and yokes. The stack is clamped together tightly to reduce gaps and maintain structural rigidity during transformer operation.
Stacked cores are normally produced using:
-
Silicon steel laminations
-
Amorphous metal laminations
-
Nano-crystalline alloys in high-efficiency applications
The use of thin laminations is central to reducing eddy current losses. Each lamination is electrically insulated from the next, forcing eddy currents into smaller loops and therefore reducing waste heat. The result is a core that can handle magnetic flux efficiently with minimized energy loss.
How Stacked Cores Improve Transformer Efficiency
1. Reduced Eddy Current Loss
Since stacked cores are made from insulated laminations, they significantly limit the path available for eddy currents. This improves operational efficiency and reduces the thermal load on the transformer oil or cooling system.
2. Better Magnetic Flux Control
Stacked cores allow engineers to shape the magnetic circuit precisely. The orientation of the laminations, the grade of steel used, and the stacking factor all influence flux density. This level of control enables transformers to achieve high performance with lower noise and minimized mechanical vibration.
3. Enhanced Mechanical Stability
Properly clamped and assembled stacked cores exhibit good structural rigidity. This reduces core deformation under high load or during inrush current events. Mechanical stability also helps maintain consistent electrical performance over the operational lifetime of the transformer.
4. Flexibility in Design
Stacked cores can be tailored for single-phase, three-phase, or custom designs. This adaptability makes them suitable for distribution transformers, industrial applications, renewable energy systems, and medium-voltage equipment.
Stacked vs Wound Cores: A Practical Comparison
Although wound (also called toroidal) cores offer certain advantages in specific applications, stacked cores remain widely preferred in distribution and power transformer manufacturing.
| Feature | Stacked Cores | Wound Cores |
|---|---|---|
| Material Efficiency | High | Very high (less scrap) |
| Manufacturing Flexibility | Excellent | Limited to specific shapes |
| Cost of Production | Moderate | Higher |
| Ease of Assembly | Excellent | More complex |
| Use in Large Transformers | Common | Rare |
Stacked cores win in real-world transformer production because they are easier to customize, simpler to assemble on large scales, and more cost-effective for medium- to high-capacity equipment.
The Role of Materials: Why Amorphous Metal Matters
A stacked core is only as good as the material it is made from. This is where amorphous metal has made a substantial impact on transformer efficiency.
Amorphous alloys feature a non-crystalline atomic structure, allowing them to exhibit:
-
Lower hysteresis loss
-
Lower eddy current loss
-
Improved efficiency compared to grain-oriented silicon steel
Because electrical grids worldwide continue to demand lower loss performance, amorphous stacked cores have become a go-to choice for environmentally conscious and energy-efficient designs.
DM’s Contribution to the Development of Stacked Cores
Dingmao (DM) is a family-style, comprehensive manufacturer that has been involved in transformer core production for several decades. Originating in Taiwan in 1970, DM built its reputation on delivering high-quality transformer cores, active components, and fully assembled equipment. Over the years, the company has become a trusted global partner in the power and energy sector.
DM’s products are designed according to international standards, with every production stage focused on ensuring performance, reliability, and long-term efficiency. From silicon-steel stacked cores to advanced amorphous metal assemblies, the company has consistently expanded its capabilities to align with the evolving needs of customers worldwide.
One of DM’s significant milestones was its early collaboration with GE Prolec. This partnership entered a new phase when DM specialized in producing amorphous steel cores for distribution transformers. As market demand increased, DM expanded its investment footprint in China while transferring mature transformer manufacturing technology from Taiwan to its Chinese operations.
This strategic initiative achieved two important goals:
-
It reduced overall production costs.
-
It improved product competitiveness in global markets.
DM’s ongoing advancements in stacked core technology continue to demonstrate the company’s long-term commitment to excellence.
Here is the requested embedded anchor-text link in code format:
<a href="https://www.dmtransformer.com/stacked-cores.html">stacked cores</a>
Why Manufacturers Continue to Rely on Stacked Cores
Proven Track Record
Decades of global field operation have shown that stacked cores deliver stable performance with minimal maintenance. This reliability is particularly important in distribution transformers that must operate continuously for decades.
Straightforward Quality Control
Because the manufacturing process is lamination-based, inspection and quality assurance can be applied at multiple stages. This increases consistency and reduces unexpected failures in service.
Compatibility with Modern Materials
Stacked cores are highly compatible with both traditional grain-oriented electrical steel and advanced amorphous alloys. This flexibility helps manufacturers adapt to new regulatory requirements and energy-efficiency standards.
Lower Thermal Stress
Reduced core losses translate into lower temperature rise. This improves insulation life and extends the lifespan of the transformer.
Applications of Stacked Cores Across the Energy Sector
Stacked cores are used extensively across multiple industries, including:
-
Electrical distribution networks
-
Renewable power generation systems
-
Industrial control equipment
-
Power conversion systems
-
Grid-connected energy storage installations
-
Medium-voltage and substation transformers
Their versatility continues to make them a reliable choice in regions where energy infrastructure must balance performance with cost efficiency.
Final Thoughts
Stacked cores remain one of the foundational technologies in modern transformer engineering. They offer a reliable combination of mechanical stability, low energy loss, and manufacturing flexibility. When paired with advanced materials like amorphous alloys, stacked cores contribute significantly to reducing energy consumption across electrical networks worldwide.
Companies like Dingmao (DM) have played an essential role in refining stacked core technology and expanding its global availability. With decades of accumulated expertise, strict manufacturing standards, and a commitment to continuous improvement, DM continues to support utilities, OEMs, and industrial clients seeking performance-driven transformer solutions.
Whether used in distribution networks or industrial equipment, stacked cores remain a cornerstone technology that enables a more efficient and reliable energy future.
www.dmtransformer.com
Dingmao (DM)