With the global "dual carbon" goal, the trend of combining building energy conservation with renewable energy is becoming more and more obvious. BIPV (Building Integrated Photovoltaics) is a combination of buildings and solar power generation. It can not only achieve green power generation, but also has the function of building components, becoming one of the key directions for the development of green buildings. Among the many BIPV solutions, choosing the right BIPV solar module is related to the efficiency, cost and aesthetics of the entire project. So, what are the types of BIPV solar modules? Which scenarios are they suitable for? Have you chosen the right one? This article will analyze it in detail for you.
1. What is a BIPV solar module?
BIPV solar modules refer to a technical solution that directly integrates photovoltaic modules as building materials into the building shell (such as roofs, curtain walls, shading systems, etc.). This type of module not only has the function of solar power generation, but also can assume the basic functions of the building skin, such as shading, heat insulation, sound insulation, waterproofing, windproofing, etc.
Compared with the traditional "BAPV (Building Applied Photovoltaics), BIPV is incorporated into the building structure during the design stage, with higher integration and aesthetics.
2. Main types of BIPV solar modules
BIPV solar modules are mainly classified according to their installation location, photovoltaic material type and light transmittance. Below we introduce them in detail according to the use scenario and material type.
1. Classification by installation location
1.1 Roof-type BIPV modules
This type of module is usually used for newly built or renovated slope roofs and flat roofs, which can completely replace traditional roof tiles or metal roof panels. Roof-type BIPV is currently the most common and mature BIPV application form.
Features:
Perfect integration with the building roof to reduce floor space
Can be deployed over a large area with high power generation efficiency
Easy to install and maintain
Representative products:
Colored steel tile BIPV modules
Tile BIPV modules
Flexible film BIPV modules
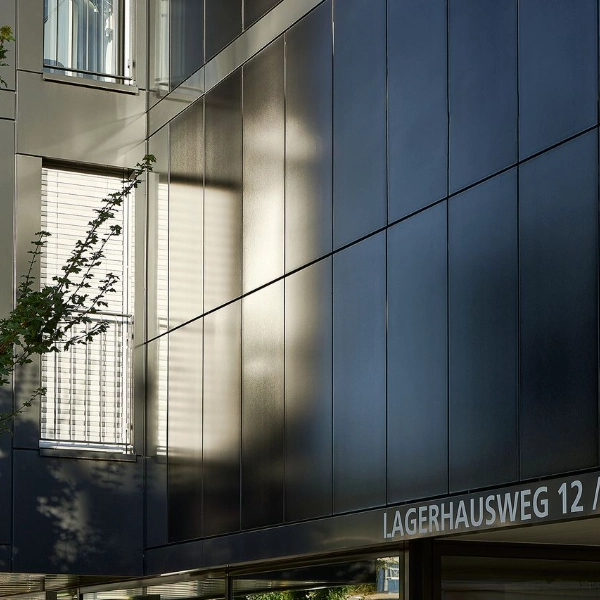

1.2 Curtain wall BIPV modules (facade photovoltaics)
BIPV curtain wall modules are mainly used for building facades, which are both decorative and can achieve vertical power generation. Commonly used in large commercial buildings, office buildings, government buildings and other projects.
Features:
Partially replaces glass curtain wall, good visual effect
Closely integrated with the building facade to enhance the beauty of the building
Size, transmittance and color can be customized according to design requirements
Representative products:
All-glass photovoltaic curtain wall components
Colored photovoltaic glass components
Transparent photovoltaic glass components
1.3 Shading system BIPV components
Install photovoltaic components in skylights, sun panels, sunshade blinds and other locations, taking into account the functions of sunshade, lighting and power generation.
Features:
Highly integrated building shading system
Power generation and shading functions coexist
Applicable to corridors, carports, landscape components, etc.
Representative products:
Glass sandwich components
Photovoltaic blinds components
2. Classification by photovoltaic material type
The photovoltaic materials used in BIPV components determine their performance, appearance and adaptability, which are mainly divided into the following three categories:
2.1 Crystalline silicon BIPV components
Including monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon, crystalline silicon components are still the mainstream material of BIPV at present, with high conversion efficiency and durability.
Advantages:
High photoelectric conversion efficiency (about 18%-22%)
Mature technology, long life (up to 25 years or more)
Low cost
Disadvantages:
Not easy to transmit light, relatively poor aesthetics
Heavy components, requirements for building structure
Applicable scenarios:
Roofs, awnings, some curtain walls that do not require lighting
2.2 Thin-film BIPV components (such as CIGS, amorphous silicon)
Thin-film solar cells are a flexible, lightweight photovoltaic material that can be made into a variety of colors and shapes, especially suitable for building facades or skylight projects with high requirements for aesthetics and light transmittance.
Advantages:
Beautiful appearance, can be made into colored components
Flexible structure, suitable for curved buildings
Good low-light performance, adaptable to cloudy and scattered light environments
Disadvantages:
Low conversion efficiency (about 10%-15%)
Relatively high cost
Applicable scenarios:
Glass curtain wall, lighting roof, sun room
2.3 Perovskite BIPV components (emerging technology)
Perovskite is a new type of photovoltaic material with extremely high theoretical conversion efficiency and excellent color expression. It is still in the stage of technical research and development and small-scale application.
Advantages:
High conversion efficiency potential (theoretically can exceed 25%)
Can be made into a variety of colors, translucent components
Suitable for customized, high-end architectural design
Disadvantages:
Stability and life still need to be improved
Not yet commercially available on a large scale
Applicable scenarios:
High-end building facades, characteristic landscape photovoltaic components
3. How to choose the right BIPV solar module according to needs?
3.1 Clarify the purpose of the building and the power generation goal
Different types of buildings have different expectations for BIPV systems:
Residential buildings: focus on beauty, cost and sunshade performance, and choose colored glass or roof BIPV components.
Industrial plants: more attention should be paid to power generation efficiency and cost return, and crystalline silicon roof-type modules are suitable.
Commercial complexes and office buildings: architectural image and lighting requirements need to be considered, and curtain wall and translucent modules are suitable.
Public buildings and municipal facilities: landscape design and power generation can be taken into account, such as the use of sunshade or artistic BIPV systems.
3.2 Consider the building orientation and climate environment
South-facing roofs and south-facing curtain walls are the best installation directions;
Areas with heavy haze or frequent rainy weather are suitable for thin-film modules;
High temperature or snowy areas need to pay attention to the temperature coefficient and load capacity of the modules.
3.3 Pay attention to structural safety and architectural coordination
Check whether the building structure can bear the weight of the modules;
The size, color, and light transmittance of the modules need to be coordinated with the appearance of the building;
Some projects may require customized sizes or non-standard shapes.
4. Future development trend of BIPV modules
BIPV is developing in the direction of "higher efficiency, more beautiful, and smarter":
Aesthetics: more colored glass and patterned BIPV modules will appear, making them part of architectural art;
High integration: highly integrate photovoltaic modules with insulation, waterproof layer, and structural parts to simplify the construction process;
Intelligent operation and maintenance: combined with the Internet of Things to achieve remote monitoring, intelligent cleaning and energy efficiency optimization;
Application of new materials: emerging materials such as perovskite and flexible carbon materials will be gradually commercialized, bringing more design possibilities.
Under the wave of carbon neutrality and green buildings, BIPV is not only an energy-saving tool, but also a bridge for dialogue between architecture and nature. Only by choosing the right type can we truly achieve the triple unity of green, economy, and aesthetics. In the future, let us look forward to more innovative BIPV solutions to inject vitality of sustainable development into the city.
www.fgnexsolar.com
fgnexsolar