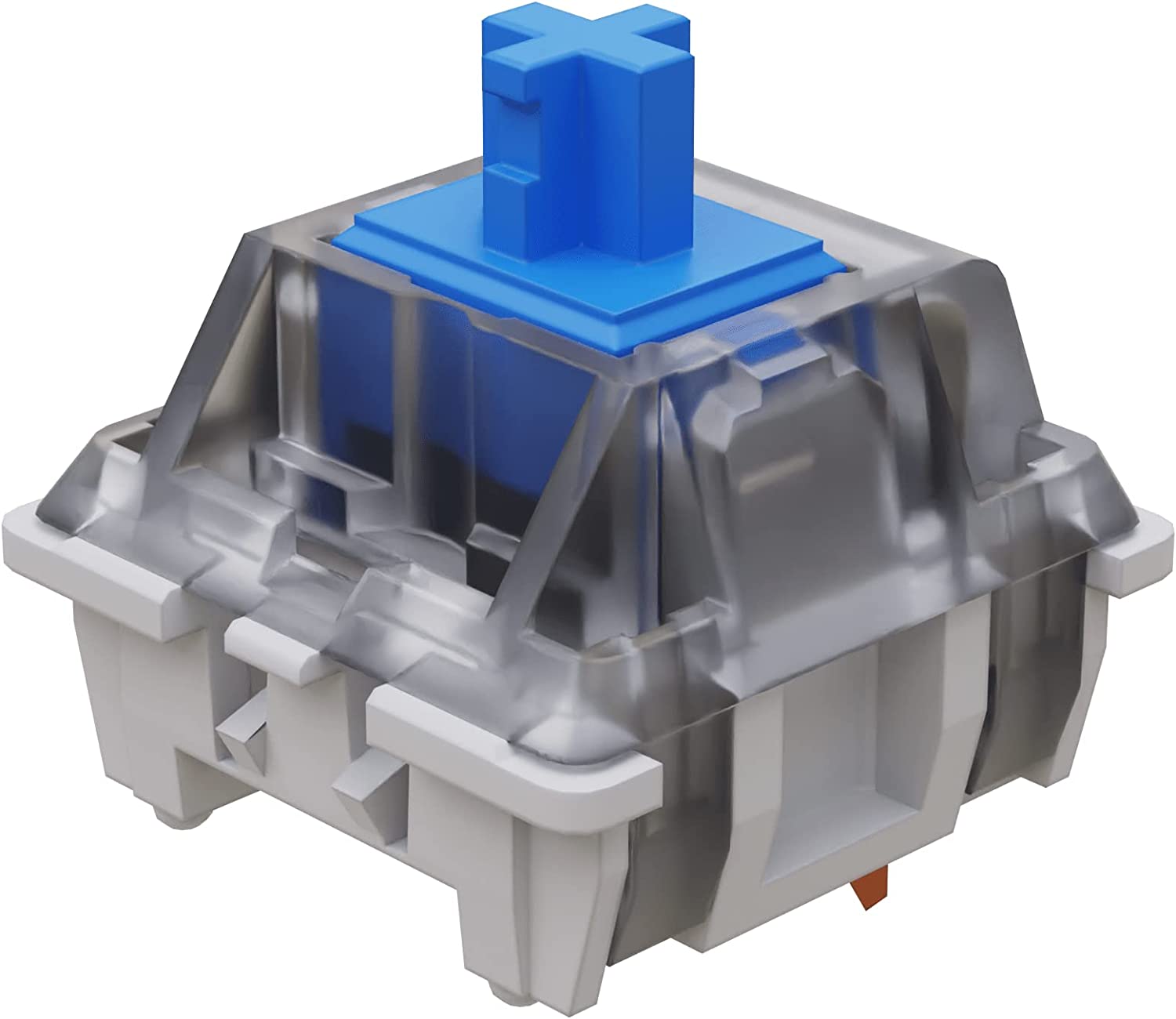
Switches are an essential component of modern technology, used in everything from household appliances to complex industrial machinery. But how do they work mechanically? In this article, we will explore the inner workings of switches, including their construction, operation, and applications.
Construction of a Switch
A switch is a mechanical device that is used to open or close an electrical circuit. It consists of several components, including a contact mechanism, an actuator, and a housing. The contact mechanism is the heart of the switch, responsible for making or breaking the electrical connection. It typically consists of two metal contacts, which are separated by a small gap. When the switch is closed, the contacts are pushed together, allowing electricity to flow through the circuit. When the switch is open, the contacts are pulled apart, breaking the circuit.
The actuator is the part of the switch that is used to operate the contact mechanism. It can take many forms, including a button, lever, or toggle switch. The actuator is connected to the contact mechanism through a series of mechanical linkages, which transmit the force from the actuator to the contacts.
The housing is the outer shell of the switch, which protects the internal components from damage and provides a mounting surface. It can be made from a variety of materials, including plastic, metal, or ceramic.
Operation of a Switch
The operation of a switch depends on its type and application. There are several types of switches, including toggle switches, rocker switches, push-button switches, and rotary switches. Each type has its own unique characteristics and applications.
Toggle switches are the most common type of switch, used in everything from light switches to electronic devices. They consist of a lever that can be moved up or down to open or close the circuit. Rocker switches are similar to toggle switches, but instead of a lever, they have a rocker arm that can be pressed on one side to close the circuit and the other side to open it.
Push-button switches are used in applications where a momentary contact is required, such as doorbells or computer keyboards. They consist of a button that is pressed to close the circuit and released to open it. Rotary switches are used in applications where multiple positions are required, such as selecting different settings on a radio or amplifier. They consist of a knob that can be rotated to select the desired position.
Applications of a Switch
Switches are used in a wide range of applications, from simple household appliances to complex industrial machinery. They are used to control the flow of electricity in circuits, allowing devices to be turned on and off, and settings to be adjusted. Some common applications of switches include:
- Light switches: Used to turn lights on and off in homes and buildings.
- Power switches: Used to turn electronic devices on and off, such as computers and televisions.
- Door switches: Used to detect when a door is open or closed, such as in refrigerators and washing machines.
- Pressure switches: Used to detect changes in pressure, such as in air compressors and hydraulic systems.
- Limit switches: Used to detect the presence or absence of an object, such as in conveyor systems and elevators.
Conclusion
In conclusion, switches are an essential component of modern technology, used in a wide range of applications. They consist of several components, including a contact mechanism, an actuator, and a housing. The operation of a switch depends on its type and application, with toggle switches, rocker switches, push-button switches, and rotary switches being the most common types. Switches are used to control the flow of electricity in circuits, allowing devices to be turned on and off, and settings to be adjusted. Understanding how switches work mechanically is essential for anyone working in the field of electronics or engineering.